AtroCore provides several entity types, each offering distinct capabilities for data management, including: Base, Hierarchy, Archive and Reference.
Base
The standard entity type that provides basic data management capabilities. This is the most commonly used entity type for most business data.
Hierarchy
The entity of the Hierarchy type differs from the Basic one in that it allows you to create child records that will inherit the values of fields and attributes from the parent. An additional Hierarchy Management panel with following fields is available for it:
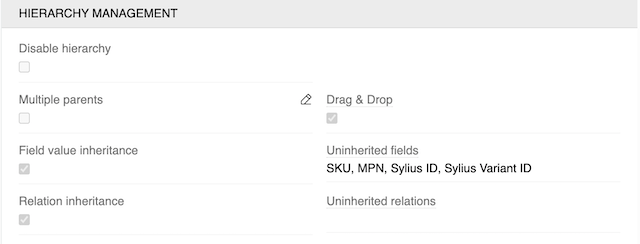
- Disable Hierarchy - converts a hierarchical entity to a basic entity with no record inheritance
- Multiple Parents - allows to link multiple parents to one child record
- Drag & Drop - this option activates hierarchy sort order, so no other sorting is possible in hierarchial navigation
- Field Value Inheritance - if this checkbox is selected, child records inherit field values from parent records
- Uninherited Fields - values for these fields will not be inherited from the parent item.
- Relation Inheritance - if this checkbox is selected, child records inherit relations from parent records
- Uninherited relations - relations with these entities will not be inherited from parent item.
For information about inheritance and hierarchies in records, see the Hierarchies and inheritance documentation.
An entity of type Relation is also created for each entity of type Hierarchy (for example, there is relation entity ProductHierarchy for hierarchical entity Product) to manage the parent-child connections between records.
Reference
Reference is an entity type that can be used to store some guide data that has no relationships to other entities and contains a small number of records. All data of this entity is stored in the configuration file.
You cannot configure access rights, use filters, or create fields of the Link or Multiple Link type for this entity type. The Code field is always created as a system field and cannot be modified.
Reference Entity Limitations Cannot be referenced by Multiple-link fields. Other entities cannot create Multiple-link fields that point to Reference entities.
Relation
When you create Many-to-Many relationships, AtroCore automatically generates a Relation entity to manage the connections between records. You can set the entity name when creating the relationship field (by default, it combines both entity names) and it contains:
- Two Link fields that reference the connected entities
- Standard tracking fields (id, created/modified dates and users).
Relation entities are also automatically created for hierarchical entities to manage parent-child relationships (e.g., ProductHierarchy for Product entity).
With the Advanced Data Management module, you can customize these Relation entities and make them accessible through the main menu.
An entity of type relation inherits the permissions from the two entities it consists of. That is, if the user has permission to create, read and edit the ProductChannel entity, but editing is prohibited for one or both entities (Channel and Product), then the user will not be able to edit the ProductChannel entity either. Thus, in order to have permission to perform some action with an entity of the Relation type, the user must be allowed this action for both the entities that form it, as well as for the Relation entity itself.
When one of the records in the related entities is deleted, the relationship record remains. Relationship record is deleted when one of the related records is permanently deleted.
Read Roles for details.
Archive
The Archive entity type is a system-only entity type used by AtroCore to store historical and system-generated data. Designed for logging and auditing purposes, it cannot be created or customised by end users beyond retention settings. Examples include:
- Import Log
- Action Excution Log
- Action History Record
Users cannot create or modify Archive-type entities, they can configure the Auto-delete period. This specifies how long archive records should be retained before they are removed automatically by the system. This setting helps to manage database size and ensure compliance with data retention policies. If the auto-delete period is not set, archive data will be retained indefinitely.
Users can choose to avoid losing data in archive-type entities and keep server storage low. This can be achieved via the ClickHouse Integration module.