AtroСore can be used as a Master Data Management (MDM) system. This means that users can import data into the platform in any convenient way. Inside AtroСore, this data can then be improved, structured, and enriched if necessary, and finally exported to external systems such as marketplaces or other platforms.
Imported data can be modified during the import process. However, in some cases it is important to preserve the original data exactly as it was received and not modify it, while at the same time creating new records in other entities based on this data. This is especially relevant when data comes from multiple source systems that may differ in their field sets, data formats, or structures.
To manage such scenarios, AtroСore provides the concept of Master Data Management (MDM). With this approach, the data structure consists of three main layers: Source Entities, Staging Entity, and Master Entity.
Source Entity
A Source Entity is the initial entity (or multiple entities) into which users import unmodified or minimally modified data from one or more external systems.
- A source entity can have an arbitrary set of fields, depending on the structure of the incoming data.
- It reflects the raw or near-raw data as provided by external systems.
- Multiple source entities can exist if data is coming from different systems with different schemas.
Staging Entity (Derivative Entity)
The Staging Entity (also called a Derivative entity) is used as an intermediate layer between source data and master data.
It is a full copy of the Master Entity and reproduces its data model exactly, with only one important difference – it does not contain any mandatory or unique fields.
- The staging entity is always a single entity per master entity.
- It is linked to the master entity with a one-to-one relationship.
Create Staging entity
To enable derivative (staging) entities, activate the Enable Staging checkbox in the Master Data Management panel of the corresponding entity settings under Administration / Entities.
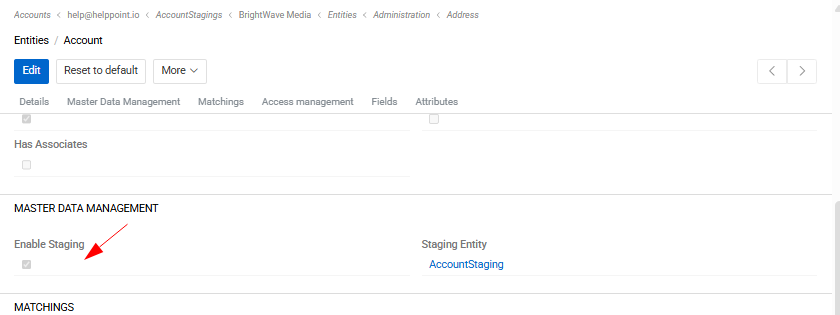
Once enabled, a staging entity is created automatically and displayed in the corresponding field.
The staging entity contains a Primary Record field, which can be used to link the staging record to the corresponding record in the master entity.
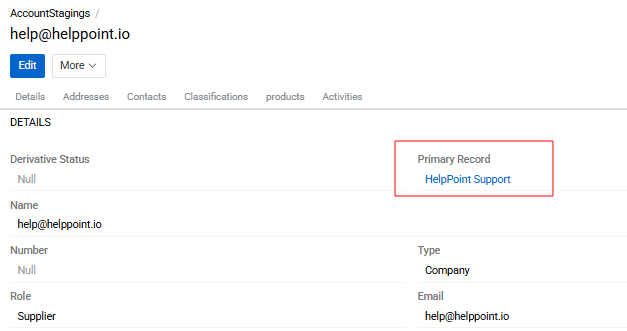
The staging entity fully inherits the fields, attributes, and layouts of the master entity. These settings cannot be modified manually for the staging entity, as they are always inherited automatically from the master entity.
Creating Staging Data from Source Data
Data is created in the staging entity automatically from the source entity (or entities) using actions of type Create or Create or Update.
From each record in a source entity, a separate record is created in the staging entity.
During this process, data can be modified, transformed, or composed from multiple fields using a script defined in the action.
The same script also defines the mapping between fields of the source entity and the staging entity.
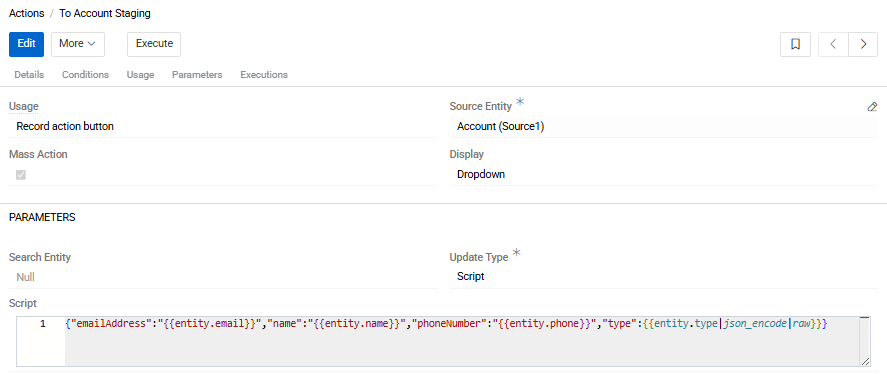
Action script allows:
- normalization and unification of data formats
- combining or splitting fields
- applying transformation logic
Data Unification and Deduplication
At the staging level, data is prepared for consolidation into the master entity. Two key processes take place here: data unification and duplicate detection.
Data unification means bringing data into a consistent and standardized format. This may include, for example, representing phone numbers in a single unified format, normalizing country codes, aligning date formats, or standardizing naming conventions. Such transformations ensure that data coming from different source systems becomes comparable and consistent.
Duplicate detection is performed using the Matching mechanism in PIM. In this mechanism, you can define matching rules that determine how potential duplicates are identified. These rules may be based on one or multiple fields (for example, name, email, phone number, external ID, or combinations of these) and can include exact or fuzzy matching logic.
After unification and duplicate detection, unified and validated data is transferred to the Master Entity, where it forms a single, consolidated, and reliable version of each record.