Table of contents
Manage entities
AtroCore offers highly flexible, scalable and configurable mechanisms that enable customers to manage and use their data efficiently without being tied to rigid structures. You have the opportunity to create your own data structure on your environment according to your own needs. This is what the Entity Manager is for. It allows you to create and delete new entities (tables) and relationships between them, add fields to entities, and configure entity parameters.
Creating and configuring entities
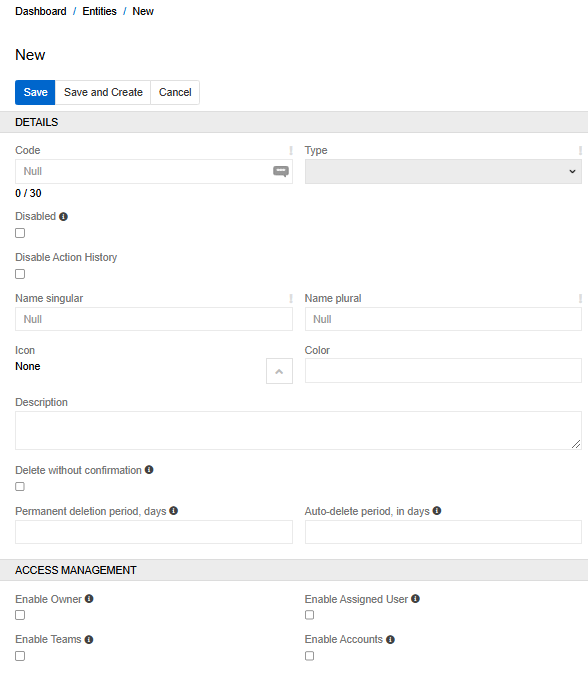
To create a new entity in AtroCore go to Administration / Entities and click on the button Create entity. The common creation window will open:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Type of the entity. Base, Hierarchy and Reference Data types are available for entities |
| Code | Entity name |
| Disabled | This option makes the entity unavailable for editing. When it is activated, the entity is available only in view mode |
| Name Singular | Singular name of the entity that will be displayed in the interface |
| Name Plural | The name of the entity in the plural that will be displayed in the interface |
| Icon | Icon to be displayed before the entity name in the left side menu |
| Color | The color of the icon |
| Delete without confirmation | If checked, the individual record is deleted without user confirmation. Deletion of multiple records is still to be confirmed |
| Permanent deletion period, days | Records for this entity are permanently deleted XX days after the deletion date. |
| Auto-delete period, in days | Records that exist longer than the specified period will be deleted from the system. |
| Access Management | In this panel, you configure roles to manage access to the entity. The following options are available here: Owner, Assigned User, Teams, Accounts |
The entity of the Hierarchy type differs from the Basic one in that it allows you to create child records that will inherit the values of fields and attributes from the parent. An additional Hierarchy Management panel with following fields is available for it:
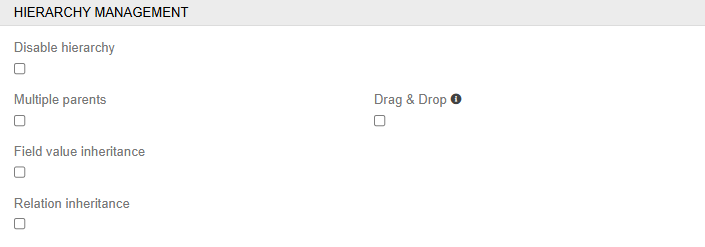
- Multiple Parents - allows to link multiple parents to one child record
- Drag & Drop - this option activates hierarchy sort order, so no other sorting is possible in hierarchy navigation
- Field Value Inheritance - if this checkbox is selected, child records inherit field values from parent records
- Relation Inheritance - if this checkbox is selected, child records inherit relations from parent records
- Disable Hierarchy - сonverts a hierarchical entity to a basic entity with no record inheritance
- Relations effecting modification date/time - Changes in these relations will cause the update of "Modified At" date and time
- Duplicatable Relations - Select the relationships that should be duplicated when duplicating an entity
After the entity has been created, you will be able to edit most of these fields. Additional fields also appear in the edit mode:
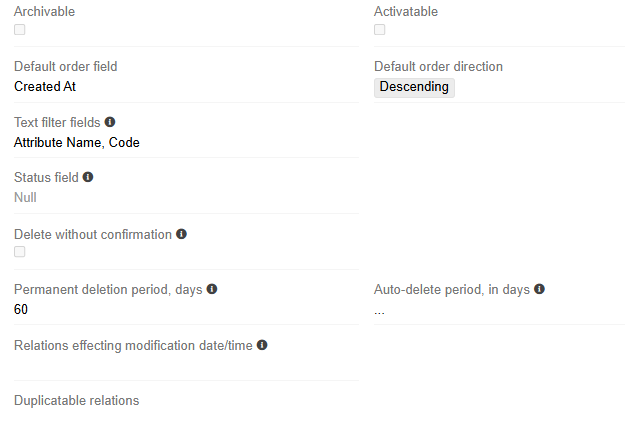
- Archivable - Enable this option to be able to archive entity records (the "Archive" field of the Boolean type is automatically added)
- Activable - his property allows you to activate and deactivate entity records (the "Active" field of the Boolean type is automatically added)
- Disable Stream - option allows you to disable change tracking (Stream) for an entity
- Default Order (field) - a field by which records are sorted in the list view
- Default Order (direction) - order of sorting
- Text Filter Fields - fields used by text search
- Status Field - Updates of this field are logged in stream
- Permanent deletion period, days - records of the entity will be permanently deleted XX days after the deletion date (60 by default)
- Auto-delete period, in days - records of the entity will be deleted XX days after the date of the last change.
You can also delete the created entity. System entities cannot be deleted. To delete an entity, click on the triangle on the right side of the table and select Delete

Reference data is an entity type that can be used to store some guide data that has no relationships to other entities and contains a small number of records. All data of this entity is stored in the configuration file. You cannot configure access rights for it, use a filter, or create fields of the link or link multiple type.
Adding fields to the entity
A new entity is created with a certain default set of fields. You can add new fields of different types or edit existing ones. New fields can be created for both custom and system entities.
in the Fields panel, you can see all the fields that are contained in the entity. System fields of an entity cannot be deleted. To add a new field click on the Create button.
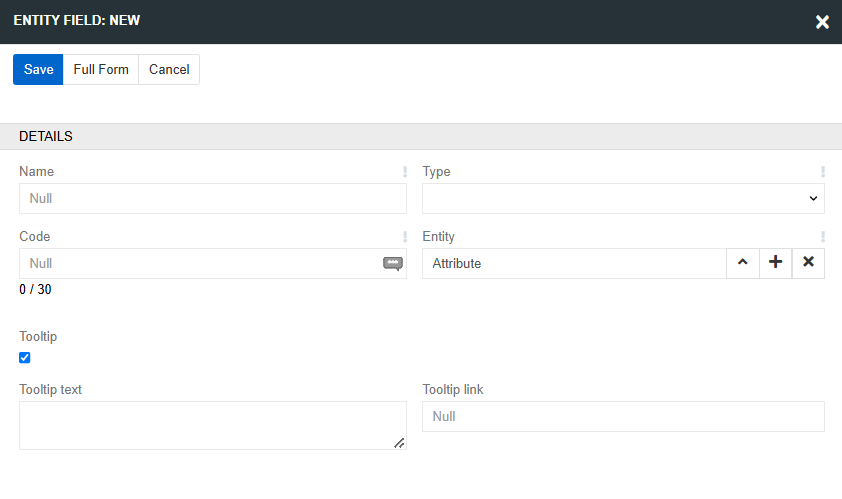
The modal window for creating a field opens. The standard set of fields includes:
- Name - field name in the main language. You can change this value later.
- Code - a unique field code within an entity. The field name is duplicated here but you can change it. The code is set only when the field is created and cannot be changed later.
- Type - select type of the new field. Depending on the selected type, the set of fields will change.
- Tooltip - select the checkbox for adding fields with text and a link of the tooltip. The tooltip is added separately for each interface language. Here you can read more about multilingualism of the tooltips.
In the opened window, enter the name of the field (it cannot be changed after creation), labels in all languages, and other properties. After that, click Save. The new field is added to the entity.
Relationships between entities
Relationships between entities are established by creating Link (many-to-one) or Multiple link (one-to-many or many-to-many) fields.
To create a many-to-one relationship go to the Fields panel, click the Create button and select the "Link" in type field. Relation management panel will appear on the modal window.
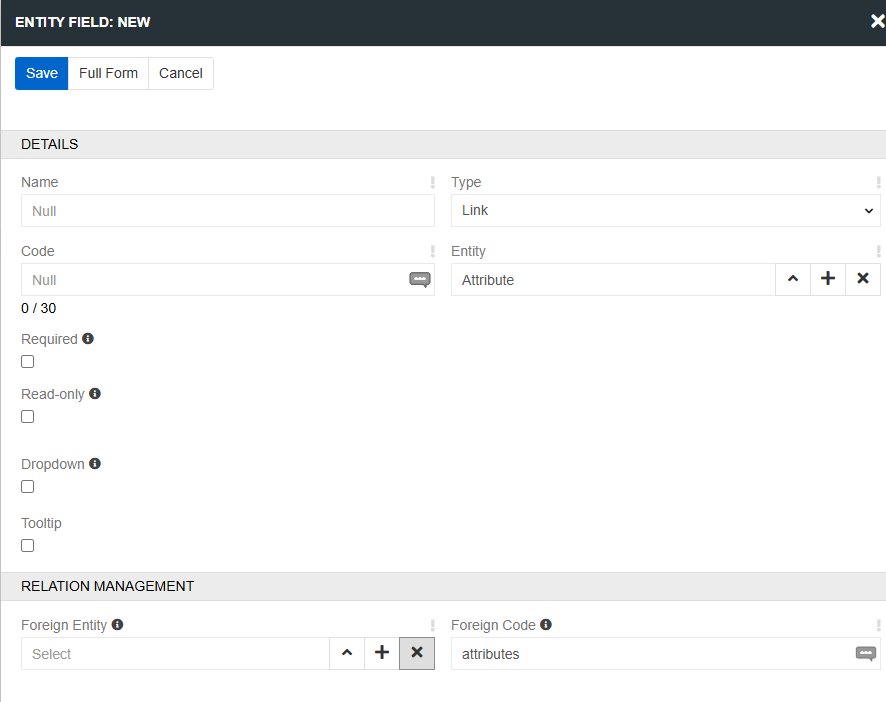
Three types of relations are available in AtroCore:
- Foreign entity - the related entity which records are referenced in the current field.
- Foreign code - the code name is used for the field created in the related entity for the backward relationship.
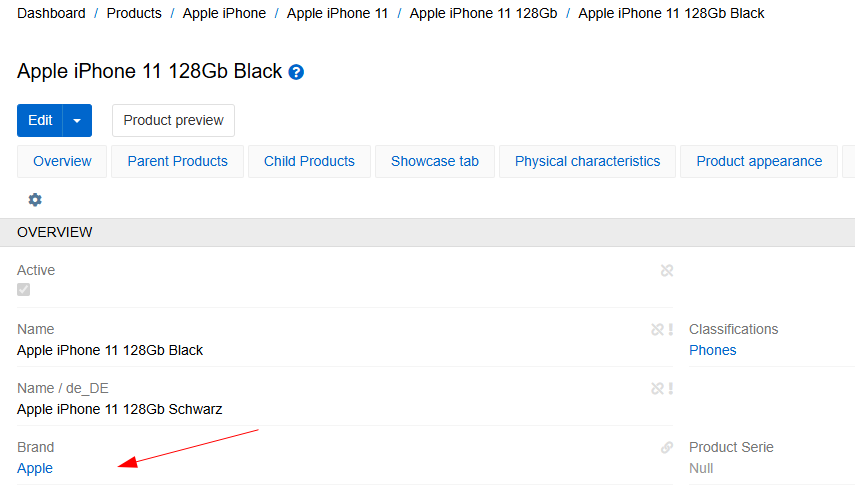
After the field of the Link type is created, you can display any field of the String type of the related entity in the entity's detail or list view (by default it is "Name"). "Brand" is the example of the field of type Link:
If an entity record can be linked to several records of another entity (for example, one Product can have multiple Categories or Channels), use a field of the Multiple Link type.
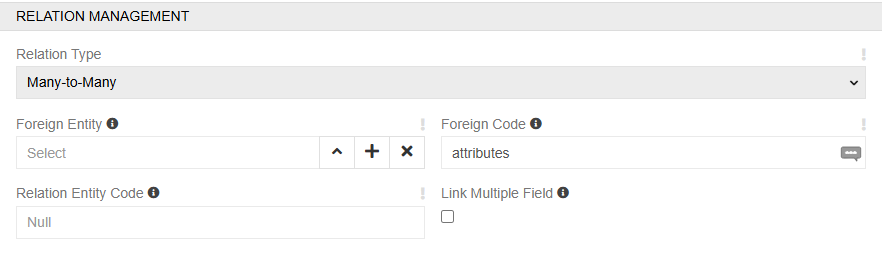
When creating a field of type Multiple link, the Relationship Management panel contains the field Relation Type, where you can select One-to-Many or Many-to-Many, depending on how the selected entities should be related. This type of field can be displayed in the entity layout as a field or a relation panel. To display it as a field, select the checkbox Link Multiple Field. This option enables a handy way to edit relations. But don't use it if you can have a large number of related records.
When you create a many-to-many relationship between two entities, an entity of type Relation is automatically created in the entity manager. The entity name is formed by combining the names of the two entities that form it. By default, the entity has two fields of the link type, which refer to the related base (or hierarchy) entities, as well as the fields id, created/modify at and created/modify by. The additional module Advanced Data Types provides the ability to edit, configure entities of type Relation and display it as a menu item.
You can change Names and Labels of created relations. Set checkbox Link Multiple Field is you want "Many" relations to be displayed as field on the detail page. Link Multiple field provides a handy way to edit relations. Don't use it if you can have a large number of related records. Link Type and Name can not be edited after creation.
Identifiers in PIM
Each entity record in has a unique ID, which is set automatically when a new record is created. PIM uses UUID v7 identifiers, which we convert to ULIDs.
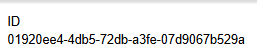
This type of identifiers allows sorting. This means that the records that were created most recently will be at the top of the table by default.
When creating a record from the user interface, you cannot set your own IDs, but it is possible when creating records by import.